SR25 takes solar radiation measurement to the next level. Using a sapphire outer dome, it has negligible zero offsets. SR25 is heated in order to suppress dew and frost deposition, maintaining its high measurement accuracy. When heating SR25, the data availability and accuracy are higher than when ventilating traditional pyranometers. In addition, SR25 needs very low power; it only consumes 1.5 W compared to the usual 10 W for ventilation. The low thermal offsets make SR25 very suitable for measuring diffuse radiation. Patents on the SR25 working principle are pending. SR25 is available with analogue millivolt output and (as SR25-D2) with digital (Modbus over RS-485) and 4-20 mA output .
Best data availability
By keeping the SR25 outer dome free of dew and frost with help of the internal heater, data availability is highly increased over traditional pyranometers, whether these are ventilated or not. The application photo in the image gallery shows the clear difference between SR25 (on the left side of the photo) versus a non-heated pyranometer without sapphire dome (on the right).
Best measurement accuracy
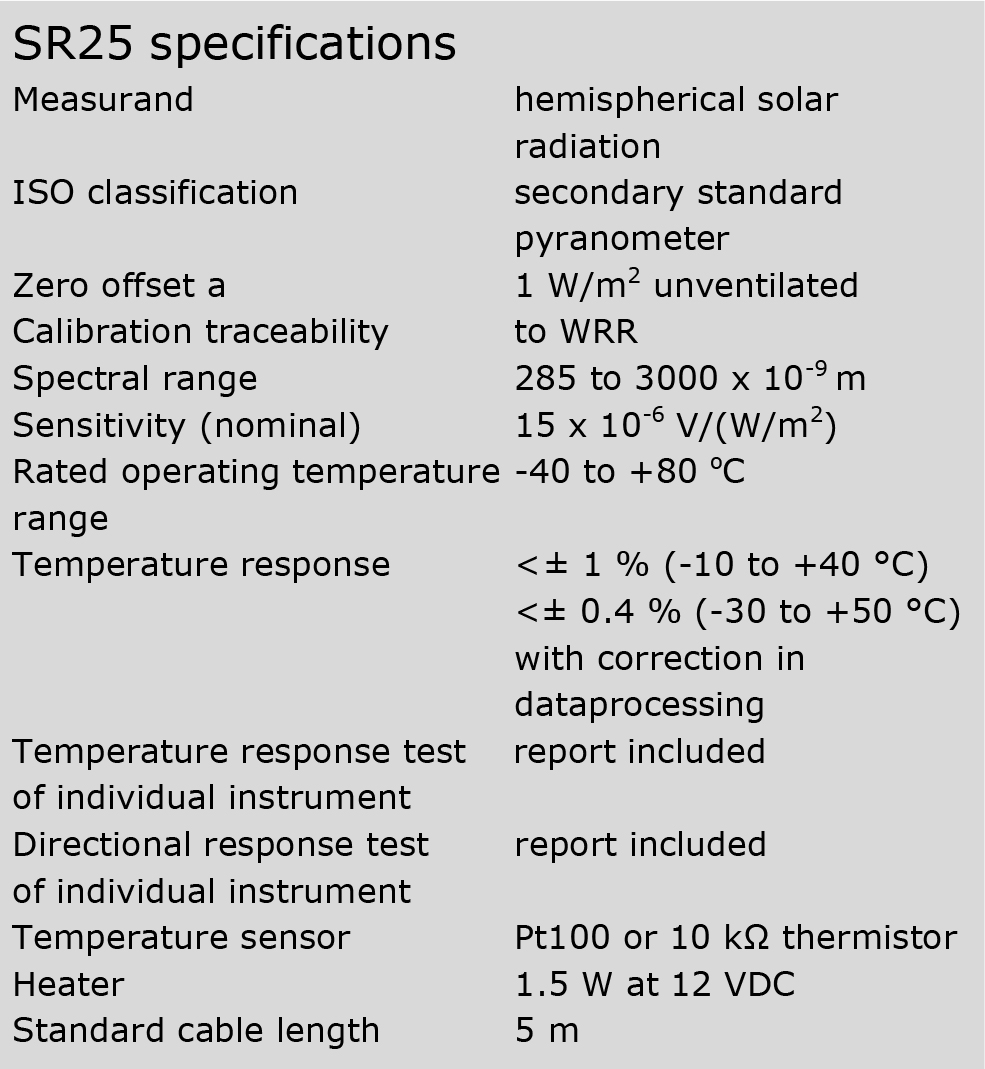
SR25 measures the solar radiation received by a plane surface, in W/m2, from a 180o field of view angle. SR25 offers the best measurement accuracy: the specification limits of two major sources of measurement uncertainty have been greatly improved over competing pyranometers: “zero offset a” and temperature response. Test certificates for temperature response and directional response are included: all sensors are tested individually for ISO 9060 compliance.
SR25 pyranometer design
SR25 has a sapphire outer dome, glass inner dome and an internal heater. It employs a state-of-the-art thermopile sensor with black coated surface and an anodised aluminium body. The connector, desiccant holder and sun screen fixation are very robust and designed for long term use. SR25 is delivered in a solid HPRC case. See the image gallery for a visual representation.
Suggested use
• all situations where ventilated pyranometers are employed
• PV system performance monitoring
• indoor PV testing with solar simulators
• airborne measurements
• diffuse measurements
• environments with dew
• environments with frost
Options
• longer cable, in multiples of 5 metres
See also
Take a look at 'SR25: The making of' for information on the development of SR25.